Alzheimer’s destructive impact and the ongoing fight for a cure

Christine John-Fuller, Alzheimer’s Association
Alzheimer’s disease, commonly known as the ‘long goodbye,’ affects families and members of the community.
“When I would go to visit my grandmother, I could tell by her eyes that she still recognized me, but she wasn’t able to talk with me anymore.”
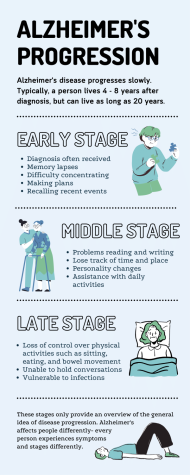
Green Hope English Teacher Ms. Kathleen Holland discovered as a high schooler that her grandmother had Alzheimer’s, marking the beginning of a 15-year battle with the disease. Alzheimer’s, an illness that affects the brain’s ability to store memories and think, has impacts that extend far beyond the patients it afflicts.
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most common forms of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of dementia cases. Although estimates vary, the National Institute of Aging suggests that more than six million Americans older than 65 have Alzheimer’s.

In the last few decades, nonprofits such as the Alzheimer’s Association have streamlined efforts to integrate communities impacted by the disease and support funding for Alzheimer’s research.
In an interview with the GH Falcon, Vice President of the Western Carolina Chapter of the Alzheimer’s Association Christine John-Fuller said that later stages of the disease impact more than just memory. Oftentimes, people with Alzheimer’s experience significant behavioral and personality changes and frequently require assistance with daily activities.
As the disease progresses, individuals begin to lose focus on their condition, relaying the grief and loss to family members. “The individual becomes dependent and stays very close to the primary caregiver, which can feel very suffocating,” said John-Fuller.
Another local organization, the Dementia Alliance of North Carolina, offers support programs, dementia navigation support and funds for dementia research grants.
Volunteer Kathy Montero leads meetings for one of the caregiver support groups every month. As a former caregiver herself, Montero resonates with others as they share their experiences and cope with the loss of loved ones.
Montero emphasized how crucial these meetings are for those surrounded by individuals with Alzheimer’s.
“No one person is the expert with this, [but] everybody collectively can provide a great forum for how to help get through caring for a loved one with dementia,” she said. “Most people [are] caregivers for more than five years. It’s a journey, we like to call it.”
Research highlights the benefits of support groups like these, which have proven to provide vital resources and reduce anxiety among caregivers.
In the scientific community, recent innovations in neuroscience research are paving the way for potential cures.
On Jan. 6, biotechnology company Biogen and partner Eisai received accelerated approval from the FDA for a treatment named Lecanemab.

The drug is an antibody that reduces the buildup of amyloid beta plaques, theorized to play a critical role in the disease, and reportedly reduces cognitive decline by 27%.
In an interview with the GH Falcon, Duke Health Neurologist Dr. Andy Liu said, “We know patients with both the amyloid and the phosphorylated tau are actually [seeing] amyloid plaques being removed from the brain, and the amount of phosphorylated tau goes down.”
Lecanemab has recently faced criticism for causing adverse side effects, including potentially fatal brain hemorrhages with the risk of bleeding largely correlated with the simultaneous use of blood thinners.
As innovations in biotechnology and neuroscience continue to expand, Green Hope students strive to contribute to the cause and make an impact in the future.
One of these students, Shreya Dey (‘24), plans to pursue neuroscience and neurodegenerative disease research after high school.
She cited her curiosity as what spurred her to pursue the field. “Diving deeper into the known and connecting dots to find a plausible solution [motivates me],” said Dey, who is enrolled in the Biomedical Innovations course at Green Hope.
“I think it’s a field that is very progressive and the idea of contributing to this science has always been within my interest,” said Dey.
Despite recent advancements, there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s. Many impacted by the disease as well as their families and friends continue to hope for a cure.
The staff of the GHFalcon would love a donation to help the journalism program at Green Hope continue to flourish. Many of our donations go to towards improving the materials that we deliver to you in electronic format. Thank you so much to those that are able to donate.

Peggy Chen is a senior at Green Hope High School, and this is her third year in the journalism program. She is thrilled to serve as the editor-in-chief and be able to report on the issues that she is passionate...