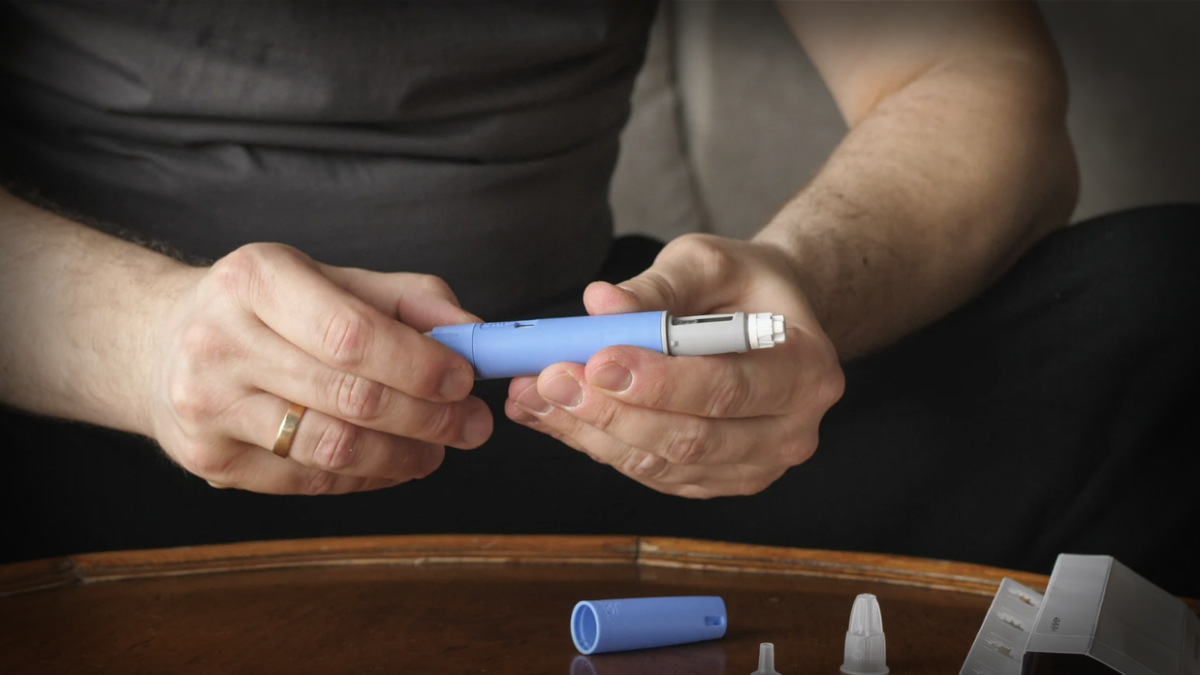
Approved in 2017, semaglutide, commonly known through medications like Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro and Rybelsus, was initially created to treat Type 2 diabetes. The medication works by mimicking pancreatic hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which triggers insulin release, regulating blood sugar levels, delaying stomach emptying and increasing satiety. Through these functions, semaglutide treats Type 2 diabetics by prompting insulin release and regulating blood sugar levels.
While semaglutide was initially created to treat diabetes, many have resorted to using the drug to lose weight. The medication can significantly aid in weight loss, as it suppresses appetite and satiety. In just two years, the drug’s popularity has risen drastically, with its amount of prescriptions within the past five years increasing by almost 10 percent due to its effective weight loss properties. Consistent semaglutide use results in an average reduction in one’s weight by 15~20 percent, with a third of its users experiencing a weight loss of 10 percent in just two months.
Semaglutide’s popularity, supplemented by influential figures such as Elon Musk and Rebel Wilson, has made it especially attractive to those seeking to lose weight. However, despite its drastic and aspirational results, semaglutide use for weight loss comes with a multitude of side effects.

As semaglutide mimics the GLP-1 hormone which impacts how the body and brain process food, common side effects such as nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, constipation and diarrhea may occur because the body’s natural processes are being manipulated by a drug. Through those immediate symptoms caused by semaglutide, subsequent side effects such as stomach pain, fatigue and dehydration may also arise. Although rare, chronic dehydration caused by semaglutide use results in irreversible kidney damage. Since the digestive system’s functions would be altered by semaglutide, the medication can also result in stomach and intestinal paralysis, meaning that the body largely loses its ability to digest food effectively.
Using semaglutide may carry heavier and longer-lasting adverse effects too. The gut and digestive system are heavily linked to the brain, and semaglutide use can disrupt the normal and healthy chemical association between the two. According to Harvard Health Publishing, gut distress can result in increased stress, depression and anxiety. When semaglutide influences the digestive system’s physiology, mental health concerns may arise, although there is not a definite correlation between semaglutide use and mental health disorders.
Medications like Ozempic and Wegovy help users drop significant weight rapidly. Rapid weight loss can result in hair loss or shedding, and as appetite is suppressed, the risk of not eating enough or consuming too few essential nutrients, vitamins and minerals arises. Nutritional deficiencies cause decreases in immunity, as well as keratin, cardiovascular, cognitive and bone health. Rapid weight loss can result in muscle loss, slowed metabolism, fatigue and gallstones— all byproducts of semaglutide use.
Since semaglutide impacts the pancreas’ function, pancreatitis may also result from the medication’s use, as the pancreas is increasingly stimulated to release insulin. As insulin levels are increased in the body, the body’s sugar levels are suddenly altered significantly, which can change the shape of the eye and result in blurred vision.
While semaglutide, a medication commercially advertised as Ozempic, Mounjaro, Wegovy and Rebelsus appeals to many due to its effectiveness in treating Type 2 diabetes and its powerful weight loss properties, many side effects result directly from the medication, and other side effects may result from the adverse effects directly linked to the medication.